
Where are you on your SWIFT ISO 20022 planning and preparation journey?
I recently took part in an Association of Foreign Banks in the UK (AFB) webinar with SWIFT where we discussed the implications and impact of the upcoming SWIFT cross border payments and reporting (CBPR) migration to ISO 20022 standards. The initial deadline for the migration was delayed for 12 months and put back to November 2022, and so it may still seem like a long way away to many. However the reality is that the time will move quickly between now and then especially with the size of the challenge and the task at hand.
It is gratifying to know that there’s a lot of help and information out there for all entities contemplating their migration journeys, especially from SWIFT who continually publish and communicate important updates and helpful guides to support institutions on their journey. But how many banks have actually started their projects already?
During the AFB webinar we asked the audience the following question to get an understanding of where the market might be in preparing or executing their journey:
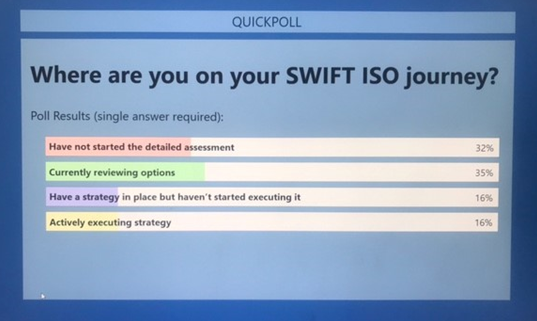
Frankly, the responses were not a major surprise with two thirds still either working on their strategy or not even begun the planning stage yet. It’s certainly what I would expect based on my own engagement experience with many entities in the market. It means there is still a lot of planning to be done, including assessing the implications of the changes required and how best to address the challenges they face.
ISO2022: There’s still a lot of work to be done as financial institutions start to define and begin their journey
The first bit of good news for those UK institutions on the Webinar who have not started to plan or are currently reviewing their options and working out their plans is the fact that – they’re not alone. Nor is this lack of progress or activity just a UK market phenomenon. There are thousands of SWIFT member entities around the world that have not begun their planning.
The second bit of good news to convey is this – there is time. Don’t Panic! There are plenty of options out there to support your journey to an ISO 20022 based future and also lots of help and expertise available. But let’s talk a little bit about what the implications are and what you, as an organization, need to do.
Payments Modernization
When one talks about payments modernisation, one sometimes can get very focused on ISO 20022 as the driver. But ISO 20022 is just one of many drivers behind a much larger industry change. Those changes include:
- Regulatory driven mandates such as PSD2 and Open Banking
- Business pressures to deliver cost efficient, customer focused process optimizations.
- New market initiatives such as international payment tracking with SWIFT GPI
- New wave of instant payment schemes that are impacting a lot of markets
- Added value services like request to pay, confirmation of payee
At the same time we continue to move towards a cashless society with greater digitization of the payments lifecycle and increases in volumes. COVID-19 has accelerated an even greater move to digital for many retail and SME businesses. Consequently, the ISO 20022 migration cannot be seen or addressed in isolation. It has to be seen as one of the key drivers behind one’s payments modernization strategy.
A fundamental change in the payment data model
However, that being said, the SWIFT ISO 20022 migration is still a key challenge at hand, and it is not as straight forward as many organizations have assumed. I still have many conversations with banks where it is viewed as just a small format change. I don’t think many of them realize that it is a fundamental change in the payment data model, and also the way payments are processed.
For example, we currently provide vital payments repair technology to a number of banks to increase their straight-through processing (STP) rates. These automated repair functions work on the current SWIFT MT standards data model, and more specifically, it focuses on 8 to 10 different fields within that data set. For ISO 20022 this set of data is expanded to circa 120 different fields. There is a certain level of expectation in the market that the need for automated repair will be reduced because ISO 20022 comes with a more structured approach to financial data. That may be the case in some situations, but we’re still expecting some systems and channels in banks to continue to populate fields incorrectly when payment orders are captured, and so the expanded data set will still be in need of repair.
We also need to be aware of the change in payments processing – and compare the ISO 20022 environment to what we’ve managed historically. In the ISO 20022 world, it’s a much more interactive exchange of information through new message types that are built to automate responses. There are automated status updates depending on whether you’re a sender or a receiver. You’ll also have to handle new advices and statement info, be it from domestic or foreign currency accounts. ISO 20022 is demanding a lot more information than we’re used to sending or receiving, be it for cross border flows, or regional and domestic market infrastructures too.
Such elevated processing requirements will have a major impact on existing systems.
However, the new standards and services also offer massive benefits to banks and the entire financial ecosystem. The provision of richer data sets, both structured and meaningful, can lead to increased STP and better reconciliation, driven by AI and automation. Ultimately, ISO 20022 will provide improved compliance and higher efficiency within organisations, all whilst promoting innovation.
So what’s not to like about that?
We need to recognize that we are moving into a new era, where the payments process is becoming much more interactive and will be much more visible to the customer. This is a rising tide, forcing us all to improve our game.
So the question is – can your current platforms handle this change and deliver the expanded capabilities required by the digital payments age?
Your SWIFT ISO 20022 Strategy
It’s important to recognize the wider implications of these changes to banking platforms. The SWIFT ISO 20022 migration is not just a catalyst for modernizing your payment processing capabilities, it may also impact other areas of processing within the organization – which means looking beyond the payments capabilities and into connected services that may be part of core, account servicing, customer information management, analytics, reporting and so on.
Organizations may also need to assess their technology platform, and i’s ability to manage the practicalities of larger data sets, such as performance and scalability. How does the system handle the XML structures? And what about how the environment ensures high STP rates – will that need to be updated?
Some organisations may have to look at a hybrid approach where they evolve their systems and aspects of their processing rather than taking a big bang approach. Some organisations are seeking to mitigate the risks of change by implementing interim translation services between the old and new standards. For this, SWIFT is offering a translation utility to help banks through the migration period and thus take some of the pressure off the meeting of difficult deadlines.
When we asked the AFB UK Webinar audience about their chosen approach we got the following response:

Just over 10% are expecting to take the translation route but almost half (45%) are still undecided on their route. Whilst it looks like the waiting game is still being played by many it’s now getting close to crunch time.
It’s time to pick your route and start your journey.